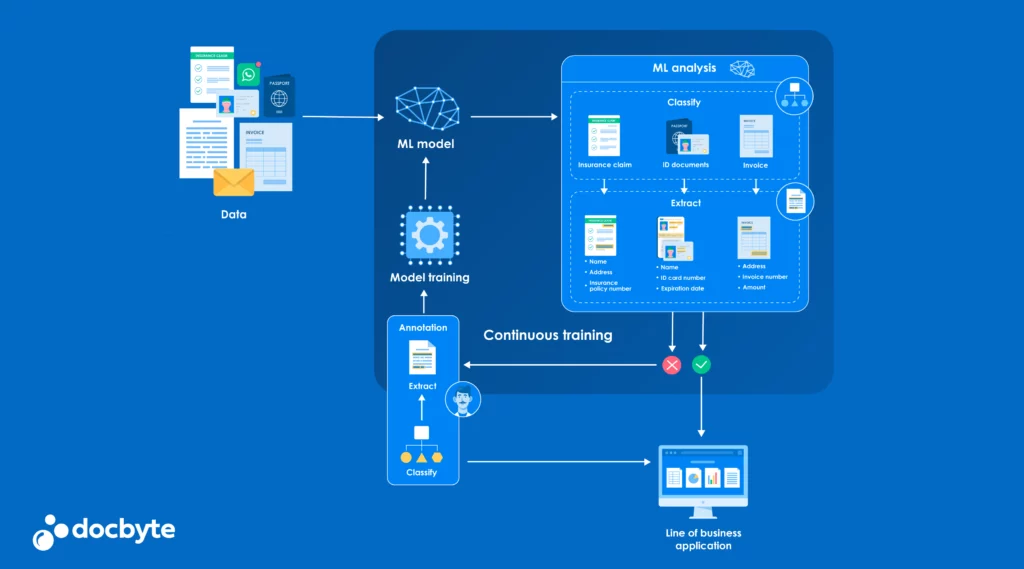
This comprehensive overview aims to guide organisations in choosing the right automation category, whether it be Robotic Process Automation (RPA) or Document Process Automation (DPA), based on their unique requirements. Ultimately, this decision improves efficiency, reduces costs, and enhances customer and employee experiences.
What is Robotic Process Automation?
Implementing automation in your organisation’s workflow is crucial for streamlining business processes and freeing employees from repetitive tasks. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) involves using bots to perform repetitive tasks, saving time and reducing human error.
RPA is suitable for simple day-to-day actions like data entry and template-based emails, making it ideal for tasks that don’t require complex decision-making.
Whitepaper - Intelligent Document Processing
What is Digital Process Automation?
Digital Process Automation (DPA) goes beyond RPA, focusing on end-to-end business processes. DPA is tailored to make workflows more efficient, allowing employees to concentrate on tasks that generate real value. Some of which offer low-code alternatives, DPA platforms enable customization to specific needs. Unlike RPA, DPA is designed to streamline complex processes and enhance workflow efficiency.
RPA vs DPA
While RPA automates small, basic tasks effectively, DPA is better suited for more complex, end-to-end business processes. The choice between RPA and DPA depends on the nature of the tasks and the level of automation required.
Banking, finance, healthcare, and logistics may benefit from DPA when dealing with intricate workflows that span multiple tasks and require customization for optimal efficiency.
When not to Use RPA
RPA is not the best solution for processes that demand cognitive decision-making or involve complex end-to-end workflows. It is most suitable for smaller, routine tasks that do not require a comprehensive understanding of the entire business process.
RPA Use Cases
- Data Entry: RPA can automate repetitive data entry tasks, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in handling large volumes of data.
- Invoice Processing: Automating data extraction from invoices and entering the information into relevant systems streamlines the invoice processing workflow.
- Basic Email Data Extraction: RPA bots can extract basic, relevant information from emails, saving time and reducing manual effort in handling unstructured data.
- Form Filling: RPA can automate form-filling tasks, such as customer onboarding forms, improving the speed and accuracy of data entry.
- Simple Customer Queries: Bots can handle routine customer queries, providing quick responses and freeing up human agents for more complex issues.
When not to Use DPA
DPA may not be necessary for organisations with more straightforward processes that can be effectively handled by RPA alone. If the workflow doesn’t require end-to-end automation or customisation is not a priority, a more concise solution like RPA might suffice.
DPA Use Cases
- Document Capture and Indexing: DPA can automate the capture of information from documents and index them appropriately, making it easier to organise and retrieve data.
- Document Routing: Automating document routing through predefined workflows ensures that documents reach the right individuals or departments on time.
- Form Processing: DPA simplifies form-based processes by automatically extracting and validating data from forms, reducing the need for manual data entry.
- Document Approval Workflows: DPA can automate document approval processes, ensuring that the necessary stakeholders review and approve documents efficiently.
- Automated Notifications: DPA can generate automated notifications or alerts based on predefined conditions, keeping stakeholders informed about the status or changes in document processes.
Why RPA isn’t a Good Fit for these Industries
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) In Banking:
While RPA excels at automating simple tasks, its limitations become evident in the complex and heavily regulated banking sector. Document Process Automation (DPA) stands out as a game-changer, specifically tailored to manage documents that need to be handled and stored according to different regulations.
These end-to-end workflows involve processes like loan approvals, account openings, and compliance documentation. DPA’s ability to customize and comprehensively automate ensures efficiency, compliance, and error reduction, addressing the shortcomings of RPA in meeting the unique demands of the banking industry.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for Finance
RPA falls short in finance-related processes where accuracy and comprehensive automation are paramount. Document Process Automation (DPA) leads by offering a focused approach to end-to-end business processes, seamlessly handling tasks such as document capture, indexing, and approval workflows.
By automating these processes, DPA allows finance professionals to concentrate on value-generating tasks, overcoming RPA’s limitations in addressing the intricate nature of document-intensive financial operations.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Healthcare
The healthcare sector’s reliance on managing vast amounts of patient records and compliance documents poses challenges for RPA. DPA proves indispensable in this context, excelling at automating complex document-centric workflows like capturing and indexing patient information, processing insurance claims, and managing medical records.
DPA’s streamlined and error-free approach addresses RPA’s limitations, ensuring operational efficiency and reducing administrative burdens in healthcare.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Logistics:
With its extensive documentation, logistics also demands a more adaptable solution than RPA can offer. Document Process Automation (DPA) is the fitting solution by automating end-to-end document processes, including capture, indexing, and routing.
DPA’s adaptability to changing regulatory standards and its ability to simplify paperwork handling make it the preferred choice in an industry where compliance with customs, shipping regulations, and documentation standards is paramount. DPA overcomes the limitations of RPA, providing a comprehensive and efficient solution for the logistics sector.
Conclusion
Choosing between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Document Process Automation (DPA) is crucial for organisations. RPA effectively automates simple tasks like data entry, while DPA is better suited for complex end-to-end business processes. Both solutions offer efficiency gains, cost reduction, and improved experiences for customers and employees.